带你认识Hutool工具包
📚简介
Hutool是一个小而全的Java工具类库,通过静态方法封装,降低相关API的学习成本,提高工作效率,使Java拥有函数式语言般的优雅,让Java语言也可以“甜甜的”。
Hutool中的工具方法来自每个用户的精雕细琢,它涵盖了Java开发底层代码中的方方面面,它既是大型项目开发中解决小问题的利器,也是小型项目中的效率担当;
Hutool是项目中“util”包友好的替代,它节省了开发人员对项目中公用类和公用工具方法的封装时间,使开发专注于业务,同时可以最大限度的避免封装不完善带来的bug。
🎁Hutool名称的由来
Hutool = Hu + tool,是原公司项目底层代码剥离后的开源库,“Hu”是公司名称的表示,tool表示工具。Hutool谐音“糊涂”,一方面简洁易懂,一方面寓意“难得糊涂”。
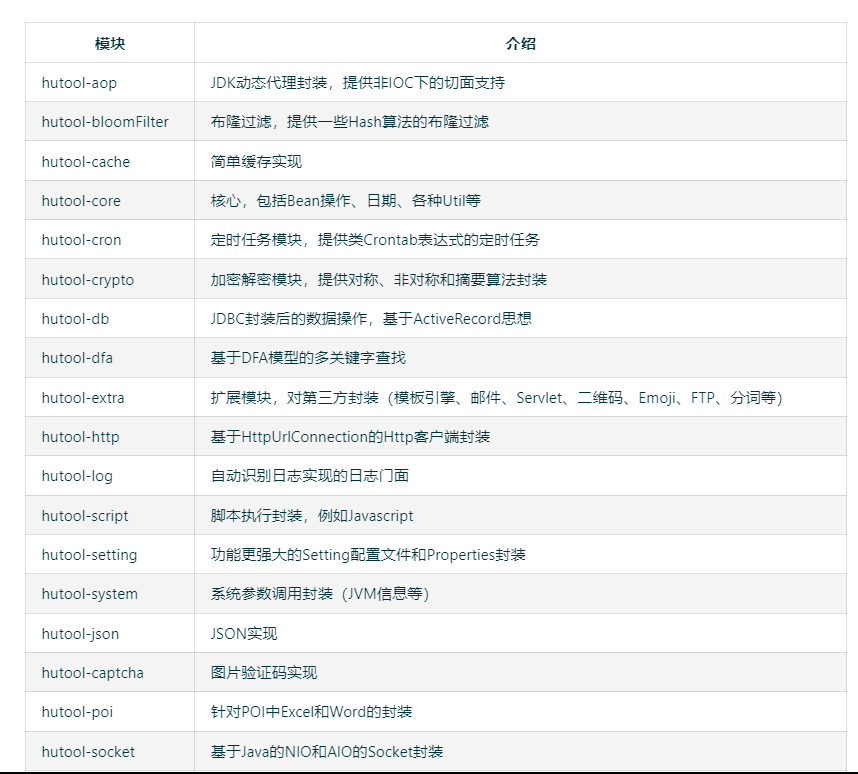
🛠️包含组件
一个Java基础工具类,对文件、流、加密解密、转码、正则、线程、XML等JDK方法进行封装,组成各种Util工具类,同时提供以下组件:
引入
Hutool-all是一个Hutool的集成打包产品,由于考虑到“懒人”用户及分不清各个模块作用的用户,“无脑”引入 hutool-all 模块是快速开始和深入应用的最佳方式。
起初Hutool只提供了两种引入方式:
- 引入
hutool-all以便使用所有工具类功能 - 引入
hutool-xxx单独模块使用
import方式
如果你想像Spring-Boot一样引入Hutool,再由子模块决定用到哪些模块,你可以在父模块中加入:
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.hutool</groupId>
<artifactId>hutool-bom</artifactId>
<version>${hutool.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<!-- 注意这里是import -->
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
在子模块中就可以引入自己需要的模块了:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.hutool</groupId>
<artifactId>hutool-http</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
使用import的方式,只会引入hutool-bom内的dependencyManagement的配置,其它配置在这个引用方式下完全不起作用。
exclude方式
如果你引入的模块比较多,但是某几个模块没用,你可以:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.hutool</groupId>
<artifactId>hutool-bom</artifactId>
<version>${hutool.version}</version>
<!-- 加不加这句都能跑,区别只有是否告警 -->
<type>pom</type>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>cn.hutool</groupId>
<artifactId>hutool-system</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
这个配置会传递依赖hutool-bom内所有dependencies的内容,当前hutool-bom内的dependencies全部设置了version,就意味着在maven resolve的时候hutool-bom内就算存在dependencyManagement也不会产生任何作用。
可以根据需求对每个模块单独引入,也可以通过引入hutool-all方式引入所有模块
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.hutool</groupId>
<artifactId>hutool-all</artifactId>
<version>5.8.11</version>
</dependency>
常见的类型转换
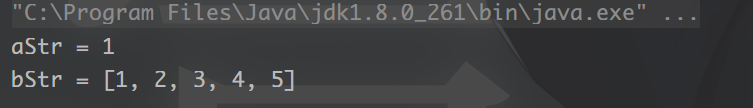
1. 转换为字符串
int a = 1;
//aStr为"1"
String aStr = Convert.toStr(a);
long[] b = {1,2,3,4,5};
//bStr为:"[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]"
String bStr = Convert.toStr(b);
运行结果:
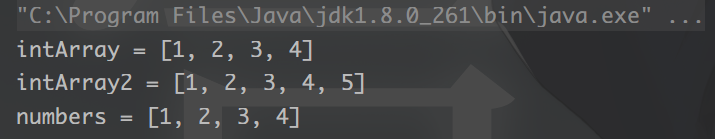
2. 转换为指定类型数组
String[] b = { "1", "2", "3", "4" };
//结果为Integer数组
Integer[] intArray = Convert.toIntArray(b);
System.out.println("intArray = " + Arrays.toString(intArray));
long[] c = {1,2,3,4,5};
//结果为Integer数组
Integer[] intArray2 = Convert.toIntArray(c);
System.out.println("intArray2 = " + Arrays.toString(intArray2));
String[] d = { "1", "2", "3", "4" };
//结果为BigDecimal数组
//Number是BigDecimal的父类
Number[] numbers = Convert.toNumberArray(d);
System.out.println("numbers = " + Arrays.toString(numbers));
运行结果:
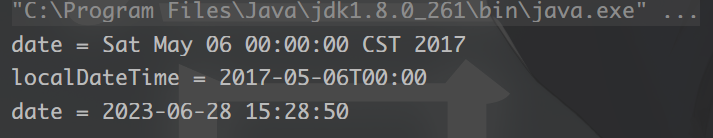
3. 转换为日期对象
String a = "2017-05-06";
// 转换为Date
Date date = Convert.toDate(a);
System.out.println("date = " + date);
// 转换为LocalDateTime
LocalDateTime localDateTime = Convert.toLocalDateTime(a);
System.out.println("localDateTime = " + localDateTime);
System.out.println("date = " + DateUtil.date());
运行结果:
4. 转换为集合
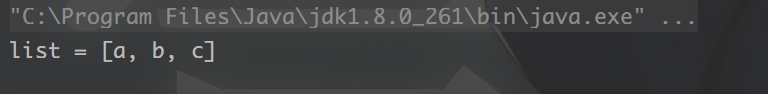
String[] strArray = {"a", "b", "c"};
List<String> list = Convert.toList(String.class, strArray);
System.out.println("list = " + list);
运行结果:
5. 转换为指定类型
User u = new User("1002","jack",18);
Person p = Convert.convert(Person.class, u);
日期时间工具-DateUtil
1. 当前时间
//当前时间 yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss
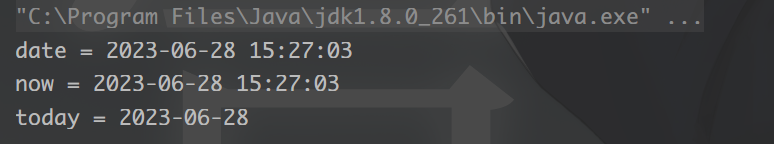
Date date = DateUtil.date();
System.out.println("date = " + date);
//当前时间字符串,格式:yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss
String now = DateUtil.now();
System.out.println("now = " + now);
//当前日期字符串,格式:yyyy-MM-dd
String today= DateUtil.today();
System.out.println("today = " + today);
运行结果:
2. 字符串转Date
- DateUtil.parse方法会自动识别一些常用格式,包括:
- yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss
- yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss
- yyyy年MM月dd日 HH时mm分ss秒
- yyyyMMdd
- yyyy-MM-dd
- yyyy.MM.dd
- HH:mm:ss
- yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS
- yyyyMMddHHmmss
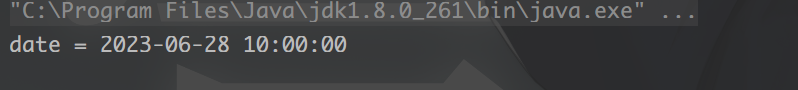
String dateStr = "2023-06-28 10:00:00";
Date date = DateUtil.parse(dateStr);
System.out.println("date = " + date);
运行结果:
3. Date转字符串
// 当前时间
Date date = DateUtil.date();
System.out.println("date = " + date);
String format = DateUtil.format(date, "yyyy/MM/dd");
System.out.println("format = " + format);
String formatDate = DateUtil.formatDate(date);
System.out.println("formatDate = " + formatDate);
String formatDateTime = DateUtil.formatDateTime(date);
System.out.println("formatDateTime = " + formatDateTime);
String formatTime = DateUtil.formatTime(date);
System.out.println("formatTime = " + formatTime);
运行结果:

4. 获取Date对象的某个部分
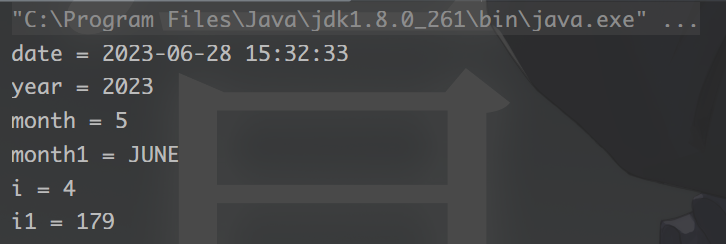
Date date = DateUtil.date();
System.out.println("date = " + date);
//获得年的部分 int类型
int year = DateUtil.year(date);
System.out.println("year = " + year);
//获得月份,从0开始计数,int类型
int month = DateUtil.month(date);
System.out.println("month = " + month);
//获得月份枚举
Month month1 = DateUtil.monthEnum(date);
System.out.println("month1 = " + month1);
//获取日期是星期几,1表示周日,2表示周一,int类型
int i = DateUtil.dayOfWeek(date);
System.out.println("i = " + i);
//获取日期是所在年的第几天
int i1 = DateUtil.dayOfYear(date);
System.out.println("i1 = " + i1);
运行结果:
字符串工具-StrUtil
//判断是否为空字符串
String str = "test";
boolean empty = StrUtil.isEmpty(str);
System.out.println("empty = " + empty);
boolean notEmpty = StrUtil.isNotEmpty(str);
System.out.println("notEmpty = " + notEmpty);
//去除字符串的前后缀
String fileName1 = StrUtil.removeSuffix("test.jpg", ".jpg");
System.out.println("fileName1 = " + fileName1);
String fileName2 = StrUtil.removePrefix("test.jpg", "test");
System.out.println("fileName2 = " + fileName2);
//格式化字符串
String template = "你好,我是{}";
String str2 = StrUtil.format(template, "test");
System.out.println("str2 = " + str2);
结果:

对象工具-ObjectUtil
1. ObjectUtil.equal
比较两个对象是否相等,相等需满足以下条件之一:
Object a = null;
Object b = null;
// true
ObjectUtil.equals(a, b);
2. ObjectUtil.length
计算对象长度,如果是字符串调用其length方法,集合类调用其size方法,数组调用其length属性,其他可遍历对象遍历计算长度。
支持的类型包括:
- CharSequence
- Collection
- Map
- Iterator
- Enumeration
- Array
int[] array = new int[]{1,2,3,4,5};
// 5
int length = ObjectUtil.length(array);
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("a", "a1");
map.put("b", "b1");
map.put("c", "c1");
// 3
length = ObjectUtil.length(map);
3. ObjectUtil.contains
对象中是否包含元素。
支持的对象类型包括:
- String
- Collection
- Map
- Iterator
- Enumeration
- Array
int[] array = new int[]{1,2,3,4,5};
// true
final boolean contains = ObjectUtil.contains(array, 1);
4. 判断是否为null
ObjectUtil.isNullObjectUtil.isNotNull
注意:此方法不能判断对象中字段为空的情况,如果需要检查Bean对象中字段是否全空,请使用
BeanUtil.isEmpty。
数字工具-NumberUtil
//封装BigDecimal中的方法来保留小数
double te1=123456.123456;
double te2=123456.128456;
Console.log(round(te1,4));//结果:123456.1235
Console.log(round(te2,4));//结果:123456.1285
//对float、double、BigDecimal做加减乘除操作
result = NumberUtil.add(te1, te2);
result = NumberUtil.sub(te1, te2);
result = NumberUtil.mul(te1, te2);
result = NumberUtil.div(te1, te2);
//保留两位小数
BigDecimal roundNum = NumberUtil.round(te1, 2);
String te3 = "1.234";
//判断是否为数字、整数、浮点数、质数
NumberUtil.isNumber(te1);
NumberUtil.isInteger(te1);
NumberUtil.isDouble(te1);
NumberUtil.isPrimes(te1)
数组工具-ArrayUtil
1. 判空
数组的判空类似于字符串的判空,标准是null或者数组长度为0,ArrayUtil中封装了针对原始类型和泛型数组的判空和判非空:
- 判断空
int[] a = {};
int[] b = null;
ArrayUtil.isEmpty(a);
ArrayUtil.isEmpty(b);
- 判断非空
int[] a = {1,2};
ArrayUtil.isNotEmpty(a);
BeanUtil
PmsBrand brand = new PmsBrand();
brand.setId(1L);
brand.setName("小米");
brand.setShowStatus(0);
//Bean转Map
Map<String, Object> map = BeanUtil.beanToMap(brand);
LOGGER.info("beanUtil bean to map:{}", map);
//Map转Bean
PmsBrand mapBrand = BeanUtil.mapToBean(map, PmsBrand.class, false);
LOGGER.info("beanUtil map to bean:{}", mapBrand);
//Bean属性拷贝
PmsBrand copyBrand = new PmsBrand();
BeanUtil.copyProperties(brand, copyBrand);
LOGGER.info("beanUtil copy properties:{}", copyBrand);
随机工具-RandomUtil
1. 获得随机数int值
int randomInt = RandomUtil.randomInt();
System.out.println("randomInt = " + randomInt);
结果:

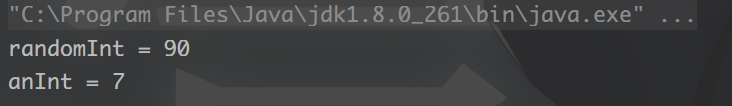
2. 获得指定范围内的随机数
int randomInt = RandomUtil.randomInt(10,100);
System.out.println("randomInt = " + randomInt);
int anInt = RandomUtil.randomInt(20);
System.out.println("anInt = " + anInt);
结果:
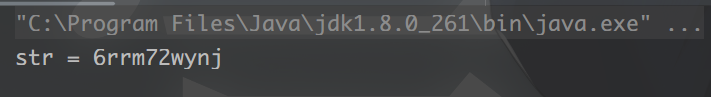
3. 获得一个随机固定长度的字符串(只包含数字和字符
String str = RandomUtil.randomString(10);
System.out.println("str = " + str);
结果:
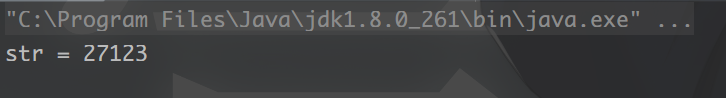
4. 获得一个只包含数字的固定长度字符串
String str = RandomUtil.randomNumbers(5);
System.out.println("str = " + str);
结果:
Hutool参考文档

